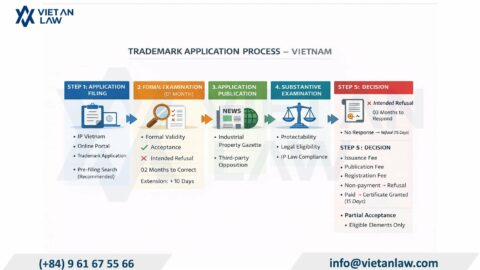
Registering trademark is increasingly popular in Vietnam. However, not every trademark application submitted to the National Office of Intellectual Property is protected. The applications were rejected mainly due to their lack of distinguishability from previously registered trademarks. In the article below, Viet An Law Firm – Intellectual Property Representative will provide basic legal advice on mistakes to avoid when registering a trademark in Vietnam.
Table of contents
According to Clause 16, Article 4 of the 2005 Intellectual Property Law, amended and supplemented in 2009, 2019, and 2022, a trademark is a sign that distinguishes the goods and services of different organizations and individuals.
Trademark registration is the mandatory process to protect trademark legally under Vietnamese law, unless the trademark recognized as famous trademark in Vietnam.
Not all trademarks registered at the National Office of Intellectual Property will be protected. According to Article 72 of the current Intellectual Property Law, a trademark is protected if it meets the following conditions:
According to the provisions of Article 73 of the Intellectual Property Law, signs that are not protected as trademarks are:
During trademark registration process, in addition to designing the trademark to meet protection standards, the trademark owner needs to pay attention to cases where signs are not protected as trademarks to avoid designing this sign on its trademark.
A trademark is considered identical to a registered trademark (opposing trademark) if that trademark is identical to the reference mark in terms of structure, meaning (content), and form of expression. A mark is considered similar to a reference mark if that mark is so similar to the reference mark in terms of structure and/or pronunciation and/or meaning (content) and/or form of expression that it causes Consumers to mistakenly believe that the two objects are the same, or that one object is a variation of the other, or that the two objects have the same origin. This is a mistake to avoid when registering a trademark.
Components are less distinguishable if they:
Famous trademarks are widely known to the relevant public in the territory of Vietnam. Currently, many businesses design trademarks that are identical/confused with famous trademarks. This confuses the origin of products and services and is an act of unfair competition to take advantage of popularity. Therefore, for trademarks that are identical/confused with well-known trademarks, the Department will refuse protection.
In addition, taking ideas from famous trademarks will not create a unique impression for consumers, and may also be punished according to legal regulations for being an act of unfair competition.
Some individuals and organizations do not carry out trademark search procedures. This is an optional procedure, but when done, it can evaluate the protection ability of the trademark and avoid trademarks that are identical/confused with previously registered trademarks. Clients can use profound search services from industrial property representatives to get the most accurate assessment.
It is important to note that the trademark on the registration declaration matches the trademark you want to protect.
In addition, the attached trademark sample must be identical to the trademark sample pasted on the registration application declaration, including size and color. The trademark sample must be presented with the size of each element in the trademark no larger than 80mm and no smaller than 8mm. The entire trademark must be presented in a trademark template measuring 80mm x 80mm. If color protection is required, all trademark samples on the declaration and attached must be presented with the correct colors to be protected.
In the International Classification of Goods and Services under the Nice Agreement, there are a total of 45 classes of goods and services. From class 1 to class 34 is the list of goods; From class 35 to class 45 is the service category. Individuals and organizations applying need to identify which types of goods and services are appropriate when submitting a trademark application.
If you have related questions or need to register a trademark, to avoid mistakes when registering a trademark, please contact Viet An Law – IP Firm for the best advice and support.