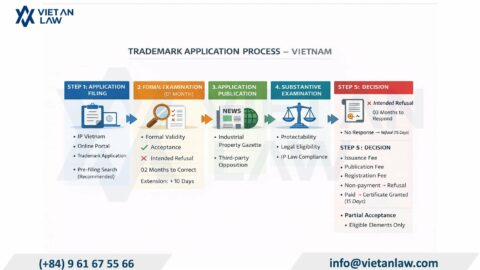
Located in South Asia, adjacent to Pakistan, China, Afghanistan and Iran, Pakistan plays an important role in connecting these regions, which is said to provide advantages for trade and investment. Pakistan has abundant reserves of natural resources, including fertile land, minerals, and water resources. These resources can be harnessed to develop industries such as agriculture, mining, and hydropower. Pakistan also has many industries that can develop economically strongly such as Pakistan can enhance agricultural production by applying modern techniques and improving irrigation systems, Pakistan has young and qualified human resources in the field of information technology, etc can promote the development of this industry or Pakistan has many attractive tourist destinations, including the Himalayas, cultural heritage sites and beautiful beaches. Therefore, more and more businesses are expanding their business scope in Pakistan, in order to be able to distinguish their trademarks from other competitors, businesses need to pay attention to trademark registration procedures. Viet An Law would like to guide customers through the preliminary procedures for trademark registration in Pakistan through the article below.

Table of contents
A trademark is a word, phrase, symbol or design used to identify and distinguish the origin of a party’s goods from other parties. A service mark is a word, phrase, symbol or design used to identify and distinguish the origin of a service rather than a good.
The Trademark Registrar (TMR) is an agency under the Pakistan Intellectual Property Organisation (IPO-Pakistan) responsible for the registration of trademarks of goods and services under the Trademark Ordinance 2001. It is an agency of the federal government, which has jurisdiction over trademarks and services within the territory of Pakistan acting as a court civil and TMR decisions can be appealed to provincial supreme courts. The trademark registry is headed by an Executive Director and its office is located in Karachi, and has a Regional Office located in Lahore.
Uniqueness: The trademark must be unique. This means that it must be able to clearly identify and distinguish the origin of the applicant’s goods or services from those of other businesses. A trademark cannot be a generic term for a product or service, a descriptive term simply describes the quality of a product or service, or something that can mislead consumers.
Availability: A trademark must not be identical or confusing to an existing trademark registered in Pakistan for similar goods or services.
Fair use: A trademark must not violate public order or morals, or be likely to mislead the public. It also cannot be obscene or offensive.
Trademarks for Goods: This is the most common type and identifies the origin of physical products. This type may include:
Service marks: Similar to trademarks for goods, these marks identify and distinguish the source of services rather than physical products. Examples include:
Collective marks: These marks are used by an association of individuals to identify goods or services provided by their members. An example could be a certification mark used by a group of craftsmen to denote products made according to specific traditional methods.
Certification marks: These marks endorse certain characteristics of a product or service, such as quality, origin, or materials. A common example is the USDA Organic certification mark for organic food products.
Account registration is mandatory to use the online brand filing system. There are two types of users as follows:
https://ipo.gov.pk/system/files/RegisterasSELFIndividualforOnlineFilingSystemVer1.1.pdf
Applicant Information:
Trademark Information:
After having all the information, the applicant needs to fill out the TM-1 form, which can be downloaded at the following link: https://www.ipo.gov.pk/trademarks-fee-forms
Statement of Use (Optional): If the applicant has commenced using the trademark in Pakistan, the applicant may submit a statement of use with evidence (e.g. product packaging, marketing materials) to potentially expedite the registration process.
Authorization (Optional): If a petitioner uses an attorney or agent to file the application, the petitioner may need a Authorization that allows them to act on the petitioner’s behalf.
Receipt of payment of fees: Currently the trademark registration fee in Pakistan is 3000 PKR
The Madrid system is a convenient and cost-effective solution for global trademark registration and management. File a single international trademark application and pay a one-time fee to apply for protection in up to 130 countries. Claimants can modify, renew or expand their global trademark portfolio through a centralized system.
Madrid Agreement:
Madrid Protocol:
The Madrid Applications include the Madrid Singles of Vietnamese origin and the Madrid Applications with Pakistani designations.
For the Madrid Application of Vietnamese origin, the applicant must submit through the state management agency for industrial property rights, i.e. the National Office of Intellectual Property of Vietnam. According to Article 25 of Decree 65/2023/ND-CP, a Madrid application of Vietnamese origin includes the following documents:
The fees include:
Additional fees depend on where the claimant wishes to protect his trademark and the number of groups of goods and services he or she wishes to register. In order to expand its geographic reach, or modify or renew its international registration, the applicant will have to pay additional fees.
If you need to file a trademark application, please contact Viet An Law for the most effective support.