Trademark registration is therefore essential for enterprises looking to do business in China and protect their intellectual property. China represents a large and lucrative economic market, but one that also faces significant challenges with illegally used trademarks. However, many foreign investors are unfamiliar with the process of registering a trademark in China, and the legal requirements and procedures involved. Viet An Law Firm hereby would like to provide the following article on trademark application in China to give professional guidance and support to clients.

Table of contents
To register a trademark in China, the following conditions must be met:
When registering for trademark protection in China, you must register the class of goods and services you wish to protect. Classifying the class of goods and services when registering a trademark plays an important role in determining the scope of trademark protection. Similar to Vietnam, currently, goods and services will be grouped based on the Nice Classification. After that, the above goods and services continue to be classified (Sub-classes) based on the classification issued by Chinese competent authorities.
Choosing a trademark model, especially for letter symbols, is very important in China – a country that uses hieroglyphs and foreign languages that need to be transcribed and translated into Chinese when registering to avoid domestic entities using translations of those trademarks as their trademarks. Therefore, one of the most effective trademark design strategies is to combine literal translation and transliteration to appear on the trademark sample upon registration.
After designing and classifying goods and services for the trademark, the applicant should search for the protection of the trademark to ensure the effectiveness of the registration procedure. Although this is not a mandatory procedure, if not done, the applicant may face a high risk of having the application refused, causing costs and money for the applicant.
China also currently uses the latest version of the Nice Classification as a basis for classification when registering trademarks.
Note: In-depth search results are for reference only and are not a basis for granting or not granting a title at the time of searching.
Foreign applicants who do not have a residence or business location in China can choose one of the following two forms:
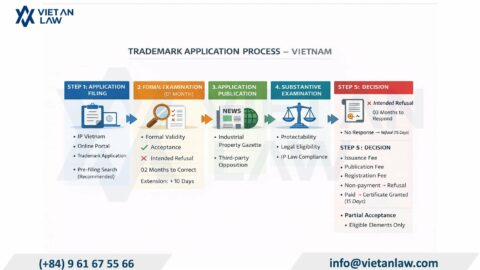
Since 2019, the formality examination time has been shortened by half compared to before. Accordingly, within 01 month from the date of filing the application, the Chinese trademark registration agency will issue a Notice of formality examination (This Notice is the Notice of valid application acceptance if the trademark registration dossier is no formal errors).
The application will be published in the CNIPA trademark gazette in Chinese (https://cas.sbj.cnipa.gov.cn/) or published in the WIPO weekly gazette if filed through the Madrid system.
However, the gazette publication time may be different between application forms. For applications through Madrid, the application will be published before substantive examination. For applications filed under the national system, the application will not be published until it has been preliminarily approved as not violating the absolute and relative basis of the preliminary examination of the trademark. This period will be significantly longer.
Objections of third parties must be filed within 3 months from the date the application is published in the CNIPA gazette or 3 months from the first day of the month immediately following the month of WIPO publication. Based on the opposition and related responses, within 12 – 18 months, CNIPA will decide to approve, partially reject, or completely reject the trademark application.
If no opposition is filed within the above deadline, or the opposition is dismissed, CNIPA will officially approve the application and issue a Trademark Registration Certificate (electronic version).
Note:
Thus, according to the newly issued law, the average time for processing trademark applications in China is about 11 months (not including the time for amending and responding to objections arising during the handling process). This time is considered quite fast compared to many countries, meeting the need for large trademark registration in this country.
The dossier of trademark application in China includes the following documents:
Note: Language used for the trademark registration dossier:
Mandatory in Chinese if submitted directly to the Chinese national registration office.
In addition to the representative service fee regulated differently by each organization, in China, the registration fee for a class (maximum 10 goods and services in a class), including state fees and lawyer fees.
In addition, the applicant must pay additional fees for responding to objections, complaints from third parties, searching the trademark, using intellectual property representation services, and notarizing documents on request, translating, expressing delivery of documents, and other services related to the dossier.
The trademark protection title is valid for 10 years from the date the registration application is approved. The extension can be performed within 06 months from the expiration date until the end of the grace period no later than 6 months from the expiration date.
Note: After having the protection title, if the owner does not use the trademark within 03 consecutive years, the protection title will be revoked.
Clients who need to carry out trademark applications in China, please contact Viet An Law Firm for the best support.