Patent is registered vibrant in Korea. South Korea is one of the world’s leading countries in the number of patent applications, demonstrating a focus on innovation and technological development. High-tech sectors such as electronics, telecommunications, biotechnology, and new energy are the focus of research and development activities in South Korea. The Korean government has been actively supporting innovation activities through preferential policies and investment in research and development. The Korean government prioritizes investment in research and development (R&D), facilitates patent activities, offers many financial support policies, tax incentives and intellectual property protection to be effectively implemented, encouraging individuals and businesses to participate in the creative process. Leading universities and research institutes attract a wide range of talent and create innovative research environments. In addition, the universities also organize international cooperation programs to help exchange knowledge and experience, improve research and development capacity. Korea also actively participates in free trade agreements and international cooperation in the field of science and technology. The exchange of knowledge, experience and technology with international partners helps to improve creative capacity and expand markets for patented products. Viet An Law would like to guide customers through the preliminary procedures for patent registration in Korea through the article below.

Table of contents
The purpose of the patent system is to promote technological development through the protection, encouragement, promotion and use of patents, thereby contributing to the development of the industry. The publication of patents leads to the accumulation and use of technology as well as the advancement of industry.
The term of the patent right begins when the establishment of the patent right is registered; It ends 20 years after the date of filing of the patent application. The validity of patent rights is subject to territorial principles; that is, it is valid only in the country where such rights are granted.
The first applicant principle and first inventor principle are two different principles that determine which applicant will be granted rights when two or more patent applications are filed for the same patent. The first applicant principle applies in Korea.
Regardless of who invented the patent, the rights of an patent are vested in the first applicant filing an application at the patent office. If two or more applications for the same patent are filed on the same day, the applicants must consult with each other and try to reach an agreement on who can patent that patent. If no agreement is reached or a consultation is not possible, none of the applicants can be granted a patent for that patent.
The first applicant principle is practical because it grants rights to the cost of technology disclosure and encourages the rapid publication of patents. This principle is consistent with the purpose of the patent system as it aims to promote industrial progress through the rapid publication of patents.
According to the first inventor principle, the rights of an patent are vested in the actual inventor, regardless of the order of application. This principle has the advantage of protecting inventors. Private inventors who don’t own businesses prefer this rule.
To apply this rule, the inventor must provide a document of the patent activities that led to the patent and ensure witnesses to the patent. The patent office must confirm the duration of the patent.
The inventor of an patent or assignee can file a patent application for that patent with KIPO. The applicant can be an individual or a legal entity.
To be entitled to priority rights, an application must be filed in Korea within 1 year from the date of submission of the priority application. Priority documents can be submitted within one year and four months from the priority date. If priority documentation is not filed within that deadline, the priority request becomes null and void.
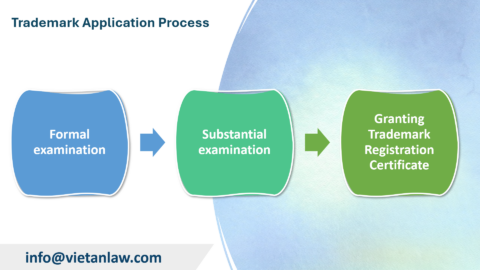
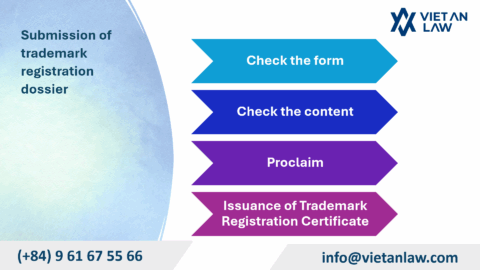
When a patent application is filed with KIPO (Korea Intellectual Property Office), it will be checked to ensure that all the requirements necessary to grant the filing date have been met. If the application does not meet the basic form requirements (e.g., the type of application is unknown, there is no applicant’s name or address, it is not written in Korean, there is no description or drawing, or the application is filed without using an agent in Korea when there is no address in Korea), The application will be returned.
After the application meets the requirements, KIPO will issue the application number and check whether other formal requirements under the Patent Law have been met. If documents or information are lacking, KIPO will ask the applicant for additional within the stipulated period. If this requirement is not complied with, the patent application will be canceled.
A patent application will be submitted for appraisal only if there is a request for appraisal from the applicant or related party within 5 years from the date of filing. If there is no request for due diligence within this period, the patent application is deemed to have been withdrawn.
Unpublished applications will be automatically published in the official gazette 18 months after the date of filing in Korea or from the priority date if priority rights are requested. Public disclosure can be made at the request of the applicant 18 months before the deadline for earlier protection of the patent application that is being infringed.
In order for a patent to be registered under the Patent Law, it must meet the requirements outlined above as follows:
If the appraiser deems there to be reasons for denying the patent application, a preliminary notice of denial will be issued and the applicant will have the need to submit a response within the deadline specified by the appraiser. If there is no reason for refusal, the appraiser will grant the patent.
When the applicant receives notice of the decision to grant a patent, the applicant must pay the registration fee within 3 months from the date of receipt of the notice.
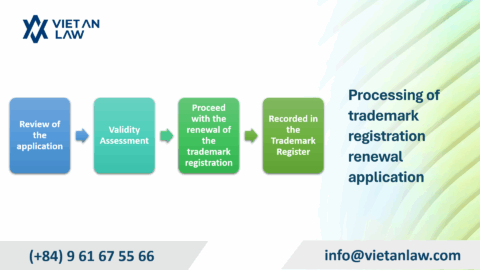
KIPO publishes the patent registration after the applicant pays the registration fee. Any person can file a petition for cancellation of the patent registration within six months from the date of publication.
| Procedure | Description | Fee (KRW) |
| Patent Application (Electronic) | 46.000 | |
| Patent Application (Paper) | a. Basic fee | 66.000 |
| b. Additional fee per page when the total description, drawings and abstract exceed 20 pages | 1.000 | |
| Request for extension of patent term, per request | 300.000 | |
| Examination fee | a. Basic fee | 18,000 (electronic)
20,000 (paper) |
| b. Additional fee for each priority claim | 18,000 (electronic)
20,000 (paper) |
|
| Request for substantive examination | a. Basic fee | 166.000 |
| b. Additional fee for each patent claim | 51.000 | |
| Annual maintenance fee | 1 to 3 years (Including patent grant fee) | 25.000 |
| 4-6 years | 56.000 | |
| 7-9 years | 124.000 | |
| 10-12 years | 265.000 |
The PCT system stands for Patent Cooperation Treaty – an international treaty that aims to create a uniform process for filing international patent applications. The system is administered by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) and has more than 150 countries participating, including South Korea.
Benefits of PCT system:
To file a patent application through the PCT system, you need to prepare a dossier that includes the following documents:
Additional documents (may require):
If you need to file a patent application in Korea, please contact Viet An Law Firm for the most effective support.