A trademark registration certificate is not only legal evidence confirming trademark ownership but also plays a crucial role in establishing a brand and fostering trust among consumers. However, not all trademarks are protected forever; in some cases, cancellation or invalidation may be necessary for a business’s strategy. In the article below, Viet An Law will provide you the information about cancellation of trademark registration certificate in Vietnam.
Table of contents
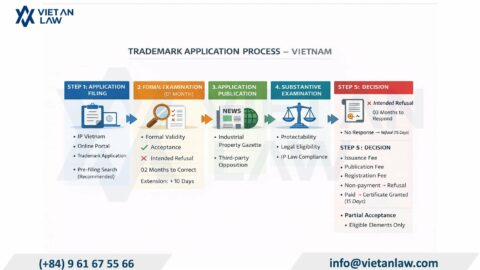
A trademark registration certificate in Vietnam is a document issued by a competent state authority to an organization or individual to establish industrial property rights to a trademark. A trademark registration certificate is valid for the period stated on the certificate. However, in certain cases, the trademark registration certificate may be partially or completely revoked.
A trademark registration certificate may be revoked in the following specific cases:
A trademark that is not used continuously for 5 years or more without a valid reason will have its registration certificate revoked. According to Article 95 of the current Intellectual Property Law, a trademark will be required to be revoked if the owner fails to fulfill the obligation to use the trademark for a long period without a valid reason, such as an economic crisis, natural disaster, or other objective factors.
The 5-year period for unused trademarks exists to ensure that certified trademarks hold genuine value and are actively used in the market. If a trademark is not used for a long time, this may lead to the trademark becoming a generic name for the product, reducing the distinctiveness and value of the trademark. Furthermore, not using the trademark may create opportunities for other organizations and individuals to register and use similar trademarks, confusing consumers.
According to Article 74 of the current Vietnam Intellectual Property Law, a trademark will be refused a certificate or cancelled if it causes confusion with a previously registered trademark.
This provision is intended to protect the rights of owners of trademarks that have been granted a certificate, ensuring that they have the exclusive rights to use their trademarks without being infringed by similar or duplicate trademarks. When a new trademark is registered that is identical or similar to an existing trademark, this not only confuses consumers but also reduces the brand value of the previously registered trademark.
Furthermore, allowing identical or similar trademarks to exist may lead to unfair competition in the market, affecting the prestige and reputation of established brands. As a result, canceling the trademark registration certificate in this case not only protects the rights of the trademark owner but also contributes to maintain a fair competition and transparency in the market.
When a trademark is no longer distinctive, this means that consumers cannot identify the origin of the product or service through that trademark, resulting in the trademark losing its commercial value and function of protecting the owner’s rights.
Reasons for a trademark to lose its distinctiveness may include the trademark becoming a generic term for a class of goods or services or widespread use without the owner’s control. When a trademark becomes a common term in the community to refer to a class of goods or services, it loses the exclusivity and distinctiveness it once had. As a result, consumers are likely to be confused by similar trademarks, and this also increases the possibility of unfair competition.
A trademark registration certificate may be cancelled when the owner declares to abandon the industrial property rights, which reflects their voluntary relinquishment of rights to the trademark. This decision may stem from many reasons, such as changing business strategy, no longer being interested in using the trademark, or not wanting to bear the costs of maintaining ownership.
When a trademark is abandoned, it means that other organizations and individuals can register and use similar trademarks, which can cause confusion for consumers. The cancellation of the certificate due to the declaration of abandonment of ownership is to protect the interests of consumers and maintain fair competition in the market.
According to Article 95 of the current Vietnam Intellectual Property Law, a trademark registration certificate might be revoked when the certificate’s holder no longer exists or is no longer in the business without a legal successor. In this case, the trademark ownership is not transferred to anyone, resulting in the trademark no longer being maintained and protected. The absence of a legal successor may cause unfair competition, as unused trademarks may create opportunities for other organizations and individuals to register and use similar trademarks, causing confusion for consumers. Therefore, it is necessary to revoke the trademark registration certificate in this case.
For collective or certification marks, if the owner fails to control – or controls ineffectively – the implementation of usage regulations, problems can arise. When the owner does not ensure that members or authorized third parties comply with these regulations, the trademark may be used improperly, diminishing its value and distinctiveness. This lack of oversight not only harms the trademark’s reputation but can also mislead consumers. In such cases, canceling the certificate helps protect consumer interests and maintain fair competition in the market. Geographical indications are no longer protected.
According to Article 95 of the current Intellectual Property Law, if a foreign geographical indication is no longer protected in the country of origin, the trademark registration certificate will also be revoked. This occurs when the geographical conditions create the reputation and quality of the product are no longer recognized. When a geographical indication is invalid, the product bearing that trademark may not guarantee the quality and origin as promised, leading to the trademark losing its commercial value. The revoke of the certificate in this case is to protect the interests of consumers and maintain fair competition in the market, ensuring that only products that meet quality standards can use the corresponding trademark.
In the context of an competitive and developing market, the cancellation of a trademark registration certificate is a necessary legal process to protect the rights of consumers and maintain fairness in businesses. Viet An Law has presented this issue in detail in the article. If you have any questions, please contact us for more detailed instructions!