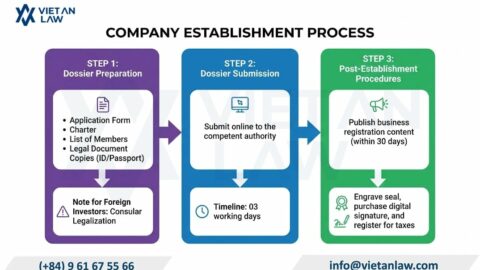
More and more international businesses and investors are realizing that setting up a company in Australia is the right move. With a strong, stable economy and a transparent business environment underpinned by a trusted regulatory system, Australia not only effectively protects investments but also facilitates access to the potential Asia-Pacific market. along with high-quality human resources and diverse skills. In addition, policies that encourage innovation and an outstanding quality of life have affirmed Australia’s position as an ideal destination for start-ups, expansion and sustainable business development on a global scale. However, what type of company can investors establish in Australia, Viet An Law would like to introduce through the article below.
Table of contents
| Criteria | Private Limited Company (Proprietary Limited – Pty Ltd) | Public Limited Company (Public Limited – Ltd) |
| Name | Must end in “Proprietary Limited” or “Pty Ltd”. | It usually ends in “Limited” or “Ltd” (except in some special cases). |
| Number of Shareholders | Minimum 1 shareholder. Maximum 50 shareholders (excluding shareholders who are employees). | Minimum 1 shareholder. There is no maximum limit on the number of shareholders. |
| Raising capital | It is not allowed to raise capital from the public through a public offering of shares. | Allowed to raise capital from the public (e.g., initial public offering – IPO), must comply with strict disclosure regulations (such as prospectuses). |
| Listing | Not listed on the stock exchange. | It is possible to register for listing on a stock exchange (e.g. ASX). |
| Number of Directors | At least 1 director. At least 1 director must be permanently resident in Australia. | At least 3 directors. At least 2 directors must be permanently resident in Australia. |
| Company Secretary | A company secretary is not required (but can be appointed). | It is mandatory to have at least 1 company secretary. At least 1 secretary must be permanently resident in Australia. |
| Reports & Audits | Financial reporting requirements are generally simpler (especially for small companies). Small companies are generally not required to audit their financial statements. | Requires more detailed and complex financial reporting and disclosures. It is often mandatory to audit financial statements and submit them to ASIC (Australian Securities and Investments Commission). |
| General Meeting of Shareholders | It is not mandatory to hold an Annual General Meeting of Shareholders (AGM). | It is mandatory to hold an Annual General Meeting of Shareholders (AGM). |
| Complexity & Cost | The procedure for setting up and maintaining is less complicated and expensive. | The incorporation and maintenance procedures are more complex and expensive due to more governance and compliance regulations. |
| Suitable audience | Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), family companies, and startups have not yet had the need to raise capital widely. | Large enterprises, companies that plan to raise capital from the public or list on the stock exchange. |
In short: