Commercial arbitration is one of the most popular dispute resolution methods in the world, especially in countries with developed economies. In Vietnam, the dispute resolution mechanism through arbitration has been established for a long time, although according to the law in each period, the organization and operation of the arbitration are different. In 2010, the National Assembly of Vietnam issued Law on Commercial Arbitration No. 54/2010/QH12 specifically regulating issues related to commercial arbitration. In the following article, Viet An Law will present an overview of the feature of commercial arbitration in Vietnam.

Table of contents
Commercial arbitration is a notion that has been around for a long time and is increasingly popular in economic life around the world. Arbitration as a method of dispute resolution is the main approach of the system of legal regulations on arbitration. According to Article 2.a of the UNCITRAL Model Law: “Arbitration means any form of arbitration with or without institutional supervision.” According to the American Arbitration Association (AAA): “Arbitration is a way to resolve disputes by submitting the dispute to several objective people to consider and resolve, and they will make the final decision, has a mandatory value for the disputing parties to implement”.
According to Clause 1, Article 3 of the Law on Commercial Arbitration 2010 stipulates: “Commercial Arbitration is a method of resolving disputes agreed upon by the parties and conducted following the provisions of this Law.” Thus, commercial arbitration can be considered from two main angles:
Arbitration is a non-governmental dispute resolution method chosen by parties to resolve commercial disputes. Arbitration is a third intermediary chosen by the disputing parties to help the parties resolve conflicts and disagreements based on ensuring the parties’ right to self-determination.
In essence, commercial arbitration is a method of resolving commercial disputes that do not carry the will of state power but is resolved through the decision of a commercial arbitrator according to flexible procedures, a dispute resolution is carried out by special institutions. Therefore, arbitration has some of the following basic characteristics:
This is a judicial body that has the authority to resolve disputes arising in commercial activities and is regulated by law. Arbitration is a jurisdictional body because conducting arbitration procedures is a regular and main activity of arbitration centers. These are centers with legal status, their own seals and accounts with a clear and strict organizational structure. As well as the court, after resolving the dispute, the arbitration tribunal will issue an arbitration award. This judgment is legally binding on the parties and is guaranteed to be enforced with the support of the enforcement agency (when requested).
The agreement is the premise for the award and there cannot be an arbitration award that goes away the agreed elements. Therefore, in principle, the arbitrator’s authority is not limited by law, parties can choose at any time any ad hoc or regulatory arbitrator in the world to resolve the dispute. However, once agreed upon, the arbitration award is binding and obligates the parties to implement it.
The parties have the right to choose the arbitrator, arbitration procedural rules, and applicable law to resolve disputes… The method of resolving disputes by commercial arbitration ensures the litigants’ right to self-determination is higher than the method of resolving disputes in court.
Ad hoc arbitration is a form of arbitration established to resolve specific disputes and is dissolved when the dispute is resolved. Permanent arbitrators are arbitration organizations that have a stable headquarters, and a list of arbitrators, and operate according to their charter.
Due to the nature of the proceedings, the court can execute at many levels of trial, so a judgment declared by the court can be appealed, protested, and resolved according to the appellate, cassation, and retrieval procedures. Therefore, if the dispute is resolved in court, it will take a lot of time, effort, and money. Meanwhile, with the principle of a one-time trial, the criteria set by the disputing parties to resolve quickly, at a low cost, and avoid prolonged have been completely met in arbitration proceedings. If one party fails to comply, the other party has the right to request the court to recognize and enforce the arbitration award. This feature represents a quick mechanism for quickly and decisively resolving trade disputes.
Pursuant to Clause 1, Article 3 of the Law on Commercial Arbitration 2010 stipulates: “Commercial Arbitration is a method of resolving disputes agreed upon by the parties and conducted in accordance with the provisions of this Law.”
Article 4 of the Law on Commercial Arbitration 2010 stipulates principles on the finality of arbitration awards. Accordingly, the arbitration award is final and cannot be appealed like a judgment of the Court.
According to the provisions of Clause 4, Article 4 of the Law on Commercial Arbitration 2010, disputes resolved by Arbitration are conducted privately, unless the parties agree otherwise. This is to ensure confidentiality and avoid affecting their reputation and prestige in the market.
According to Clause 1, Article 5 of the Law on Commercial Arbitration 2010, disputes will be resolved by arbitration if the parties have an arbitration agreement. Arbitration agreements can be made before or after a dispute arises.
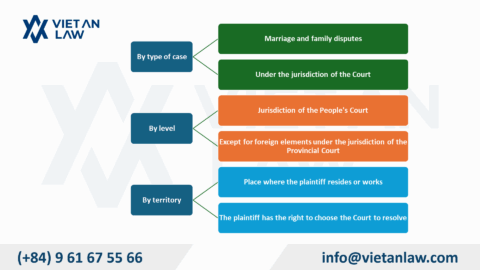
According to Article 2 of the Law on Commercial Arbitration 2010, the Arbitrator has the authority to resolve the following disputes:
Enterprises that need corporate legal advice and dispute resolution through commercial arbitration please contact Viet An Law Firm to receive the fastest and most effective support from an experienced and highly qualified lawyer.