Joint stock company and sole proprietorship are types of enterprises that have many differences from each other. Therefore, many traders have asked the question whether they should choose to establish a joint stock company or a sole proprietorship. To answer client’s questions, Viet An Law Firm offers an article about compare joint stock company and sole proprietorship in Vietnam below.

Table of contents
| No | Criteria | Joint stock company | Sole proprietorship |
| 1 | Legal basis | Chapter V from Article 111 to Article 176 of Law on Enterprises 2020 | Chapter VII from Article 188 to Article 193 of Law on Enterprises 2020 |
| 2 | Owner | Referred to as a shareholder, and can be an individual or an organization | · Referred to as sole proprietorship’s owner, and can be only an individual.
· The owner of a sole proprietorship must not concurrently owner of a household business or hold the position of general partner of a partnership |
| 3 | Member | Individuals and/or Organizations | Must be individuals. |
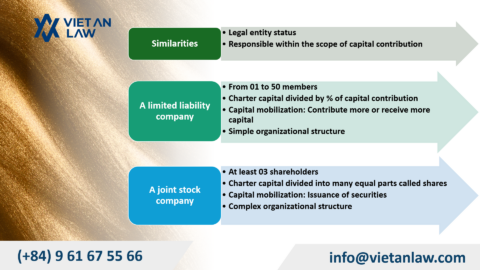
| 4 | Number of members | · Minimum: 03 shareholders
· Maximum: No limited |
Have only a member. |
| 5 | Dossier for establishing company | Include:
· An enterprise registration application form · Company’s chapter · The list of founding shareholders; the list of shareholders that are foreign investors. · A copy of documents such as: Legal document of individuals, organization; Investment Registration Certificate. |
Include:
· An enterprise registration application form · A copy of legal documents of the sole proprietorship’s owner. |
| 6 | Structure | Can be chose one of the two models below:
· General Meeting of Shareholders (GMS), Board of Directors, Board of Controllers and Director/General Director. · General Meeting of Shareholders (GMS), Board of Directors and Director/General Director |
Primary model: only include a sole proprietorship’s owner |
| 7 | Decision rights about issues of company | Issues shall be through and approved by GMS, Board of Directors | The sole proprietorship’s owner can self-decide all of the issues in the operation process of this enterprise. |
| 8 | About responsible for assets | A shareholder’s liability for the company’s debts and other asset liabilities is equal to the amount of its contributed capital to the company; | The owner of the sole proprietorship shall be personally responsible for all activities of the enterprise. |
| 9 | About the legal person | From the date on which the Enterprise Registration Certificate is issued, a joint stock company has the legal person. | Have not a legal person. |
| 10 | Capital | A joint stock company’s chapter capital is contributed by shareholders and is divided into units of equal value (shares). | The investment capital of the sole proprietorship owner is all of its assets. |
| 11 | Capacity to raise capital | Have the high capacity to raise capital, because can be published shares, bonds, and other securities. | Have the low capacity to raise capital, because can be only depended on the assets of the sole proprietorship owner and must not be issued any kind of securities |
| 12 | Rights about capital contribution to establish or purchase shares, contributed capitals | Be allowed to contribute the capital to establish and purchase shares of joint stock companies, contributed capitals of partnerships, limited liability companies. | Not be allowed to contribute the capital to establish and purchase shares of joint stock companies, contributed capitals of partnerships, limited liability companies. |
| 13 | Capicity to convert of an enterprise | A joint stock company can be converted into a limited liability company with single member or multiple member. | A sole proprietorship can be converted into a limited liability company, joint stock company or partnership. |
| 14 | Ways, and conditions to convert an enterprise | Ways to convert a joint stock company into a single member limited liability company (Article 203 of Law on Enterprises 2020)
· All shareholders convert all shares to a shareholder. · All shareholders convert all shares to an organization/ individual that is not a shareholder. · The company has only a shareholder. Ways to convert a joint stock company into a multiple member limited liability company (Article 204 of Law on Enterprises 2020): · Without raising additional capital or transferring shares to other organizations, or individuals. · Raising additional capital or transferring shares to other organizations, individuals · Transfering all or part of shares to other organizations and individuals · Only 02 shareholders remain in the company |
Conditions to convert (Article 205 of Law on Enterprises 2020):
· Be granted the Enterprise Registration Certificate. · The owner makes a written commitment to take personal responsibility for all debts. · The owner has a written agreement with the parties of ongoing contracts. · The owner has a written commitment or agreement with other limited partners to continue hiring the existing employees of the sole proprietorship. |
Thus, joint stock companies and sole proprietorships have many differences and also have their advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, depending on your needs, customers can choose the type that you think is suitable.
If clients have any questions about types of joint stock companies and sole proprietorships, please contact Viet An Law Firm for our best support!