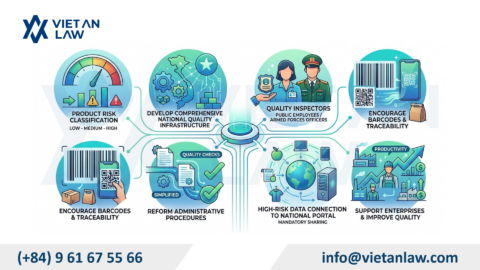
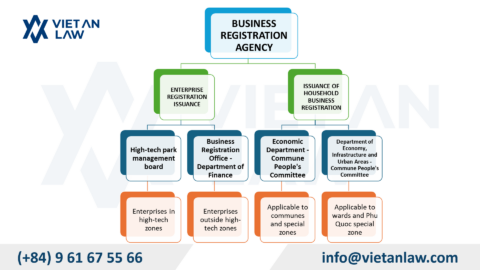
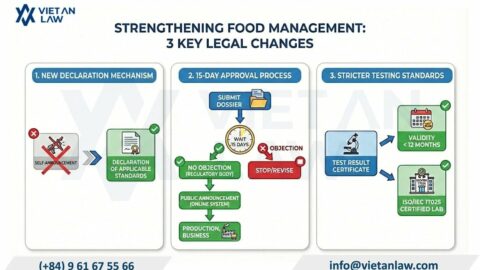
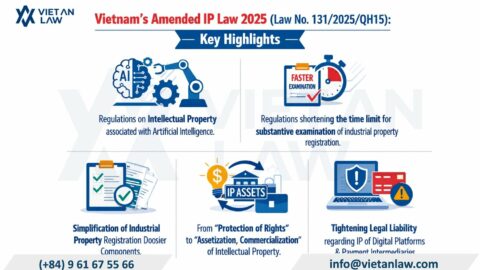
On October 1, 2023, the Supreme People’s Court issued Decision 364/QD-CA on the publication of 7 new case laws applicable from November 2023. Accordingly, these 07 newly officially announced precedents have been added to the system of case law sources in Vietnam, bringing the total number of case laws published in Vietnam to 70 case law.
Case law in Vietnamese jurisdiction has been called under the term: “precedent”. According to the definition in Article 1 of Resolution 04/2019/NQ-HDTP: “A precedent means arguments and rulings in a legally effective judgment or decision (hereinafter referred to as “judgment”) of the courts that are selected by the Council of Judges of the Supreme People’s Court and published by the Chief Justice of the Supreme People’s Court for other courts to study and apply them when deciding later cases”.
The purpose of applying case law in research and trial in Court is to ensure that cases with similar legal situations must be resolved the same. Accordingly, when there is a published source of precedent and there are similar legal issues, but the Court does not apply the precedent, the reason must be clearly stated in the judgment or decision of the Court.
Case law is recognized as a legal source of law under the Civil Code. Accordingly, precedents published according to the procedure through precedents prescribed by law can be applied as a source of law for the application of the law regime. Courts in Vietnam can study and apply officially published precedents as a legal basis in adjudication in addition to written sources of law, custom, and equity.
According to the provisions of Article 8 of Resolution 04/2019/NQ-HDTP, the effectiveness of precedents arises after 30 days from the date of publication. The 07 newly announced case laws will take effect from November 1, 2023, according to Article 2 of Decision 364/QD-CA.
Source of case law: Cassation Decision No. 15/2022/HS-GDT dated October 4, 2022, of the Council of Judges of the Supreme People’s Court on the criminal case “Kidnapping to appropriate property” for Defendant Tran Van N and his accomplices.
Legal basis related to case law: Article 169 of the 2015 Criminal Code (amended and supplemented in 2017).
Source of case law: First Instance Criminal Judgment No. 42/2018/HSST dated December 3, 2018, of the People’s Court of Dong Hai District, Bac Lieu Province on the case of “Human Trafficking” against the defendants Duong Van S and Pham Hong K, Duong Thi T1, Tran Ich C.
Legal basis related to case law:
The defendant, through an intermediary, made an offer to the victim about a job, so the victim accepted. After that, the defendant transferred the victim to another person and forced him to do work against the victim’s will to make a profit. In this case, the defendant must be prosecuted for criminal liability for the crime of “Human Trafficking”.
Source of case law: Criminal Appeal Judgment No. 86/2022/HS-PT dated February 17, 2022, of the High People’s Court in Hanoi on the case of “Human Trafficking” against defendants Trinh Thi H and Dang Thi C.
Legal basis related to case law:
The defendant committed acts of deception, promising benefits to the victim, causing the victim to trust and voluntarily follow the defendant abroad, after which the defendant handed the victim over to another person to receive money. In this case, the Court must determine that the defendant’s crime is the crime of “Human Trafficking” and not the crime of “Organizing for others to flee abroad illegally”.
Source of case law: Cassation Decision No. 40/2021/DS-GĐT dated June 23, 2021, of the High People’s Court in Hanoi on the civil case “Dispute on division of common property” between the plaintiff and Mr. Nguyen Thi D and the defendant Mr. Pham Ngoc H; people with related rights and obligations include 06 people.
Legal basis related to case law: Article 209 and Article 219 of the 2015 Civil Code.
In the case of dividing common property, which is home ownership and land use rights, one side is the elderly person who has created, managed, and used real estate in a stable, long-term manner and wishes to receive the real estate and make payments of the remaining value for other people. Real estate cannot be divided into assets. In this case, the Court must decide to hand over the house and land to the elderly person and the elderly person must pay the value of the remaining property to other people.
Source of case law: Cassation Decision No. 06/2019/DS-GDT dated March 18, 2019, of the Council of Judges of the Supreme People’s Court on the civil case “Inheritance dispute, claiming contributions raising, taking care of, preserving the house and land and claiming the house and land” between the plaintiff, Ms. Nguyen Tuy H, and the defendant, Ms. Ly Lan H1; people with related rights and obligations include 06 people.
Legal basis related to case law:
The person leaving behind the legacy of housing ownership and land use rights died before the 2013 Land Law and 2014 Housing Law took effect. Disputes over property inheritance division were resolved by the Court at the time the Land Law 2013 and Housing Law 2014 took legal effect. In this case:
Source of case law: Decision No. 755/2018/QD-PQTT dated June 12, 2018, of the People’s Court of Ho Chi Minh City on the civil matter “Request to set aside arbitration award”; The requester is Ms. Do Thi Mai T, the person with related rights and obligations is R.
Legal basis related to case law:
The employee and the employer sign an information confidentiality and non-competition agreement stating that after the termination of the labor contract, the employee is not allowed to do similar work or work that competes with the employer within a certain period. If there is a dispute, it will be resolved by commercial arbitration. In this case, the Court must determine that the dispute over the information confidentiality and non-competition agreement between the two parties is an agreement independent of the labor contract, falling under the jurisdiction of the Commercial Arbitrator.
Case law source: Cassation decision No. 06/2022/LD-GDT dated September 26, 2022, of the High People’s Court in Ho Chi Minh City on the labor case “Dispute on unilateral contract termination labor” between the plaintiff, Mr. Vuong Quoc A, and the defendant, K Vietnam Limited Liability Company.
Legal provisions related to case law:
The employee and the employer sign a definite-term labor contract. During the contract term, the employee is elected Chairman of the Executive Committee of the trade union, but his candidacy and election are invalid. At the end of the contract term, the employer issues a decision to terminate the labor contract with the employee. In this case, the Court must determine that it is correct for the employer to terminate the labor contract with the employee.
Above is the updated content of Viet An Law on Decision 364/QD-CA on the publication of 7 new case laws applicable from November 2023. Customers who need consulting, dispute resolution representation, or related civil and criminal legal advice, please contact Viet An Law for the best support.