Copyright is one of the intellectual property rights and is protected by intellectual property law. However, in reality, many acts affect copyright and infringe upon the legitimate rights of authors and copyright owners in general. What are the latest acts considered copyright infringement in Vietnam under current law? Viet An Law will answer for clients in the following article.
Table of contents
According to Clause 2, Article 4, Articles 18-20 of the Intellectual Property Law 2005 (amended in 2010, 2019, 2022), copyright is defined as the rights of organizations and individuals to works they have created or own, including moral rights and economic rights. Specifically:
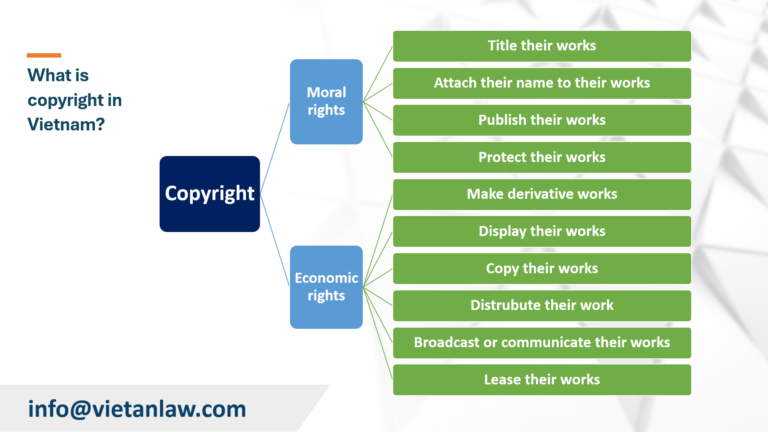
According to Clause 1, Article 6 of the Intellectual Property Law 2005 (amended in 2010, 2019, 2022), copyright arises as soon as a work is created and expressed in a tangible form, regardless of its content, quality, form, medium, language, whether or not it has been published, or whether or not it has been registered.
As such, the copyright protection mechanism is quite special because copyright protection does not depend on registration. Therefore, in reality, many authors are “subjective” and do not register their copyrights, leading to their legitimate rights being infringed.
In such cases, to protect their rights, authors must prove that they are the creators or owners of the work. Of course, proving this is not always simple, and in many cases, authors may find it difficult to prove their legitimate rights and have to accept the “loss” of their work.
Copyright infringement occurs when an individual or organization, who is not the author or has been authorized or assigned copyright by the author (collectively referred to as an unauthorized party), exercises the copyright as stated in the first part. This negatively affects the legitimate rights and interests of the author or copyright owner.
For example: “stealing” someone else’s work, publishing a work that was not created by oneself, performing a song in public (at festivals, conferences, etc., with a large audience).
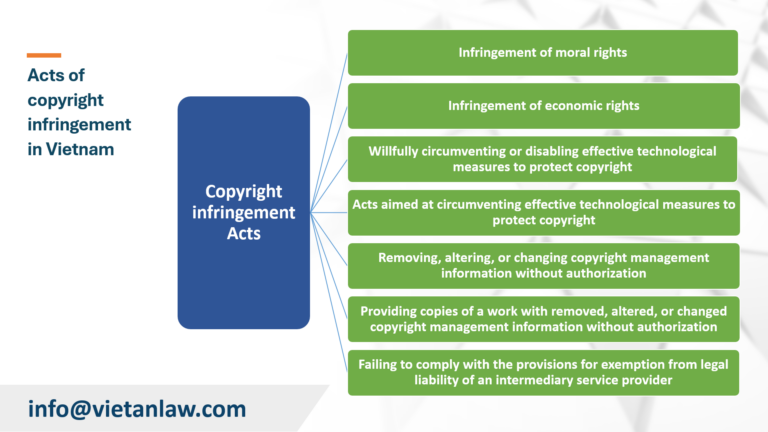
According to Article 29 of the Intellectual Property Law 2005 (amended in 2010, 2019, 2022), the copyright infringement acts include:
According to Articles 198, 202, 211, and 212 of the Law on Intellectual Property 2005 (as amended and supplemented in 2010, 2019, and 2022), authors and copyright owners can take the following measures to protect their legitimate rights and interests.
The Court is the only competent authority to apply civil measures. Therefore, to apply these measures to protect their legitimate rights and interests, the author/copyright owner has the right to personally or authorize another person to request the Court to apply civil measures. Civil measures include:
Similar to civil measures, administrative and criminal measures can only be imposed by competent authorities. However, it is important to note that these measures are only applicable to acts of copyright infringement that violate the law.
For administrative and criminal measures, authors or copyright owners need to request the competent authority when there are signs of illegal acts that infringe upon their legitimate rights and interests.
Therefore, Viet An Law has provided you with a list of the latest acts considered copyright infringement in Vietnam under current law. If you have any further questions or need legal support, please contact Viet An Law for timely assistance.