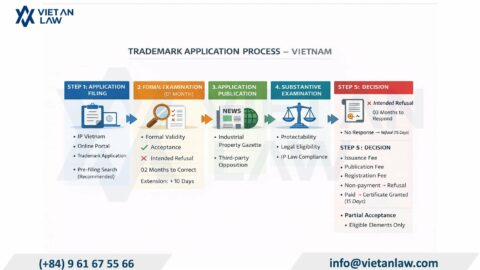
Intellectual property rights are one of the rights that attract the most attention from organizations and individuals. Vietnamese laws have been gradually changing to build a comprehensive legal framework for intellectual property, to fully ensure owners’ rights and interests. In the article below, Viet An Law would like to answer your question: “Can protect intellectual property rights for artificial intelligence?”.
Table of contents
Artificial Intelligence (AI as an abbreviation) is one of the most prominent and developed technologies today. Artificial Intelligence is a field of computer science that aims to create systems or programs that can perform tasks as intelligently as humans.
Artificial intelligence allows computers to learn, reason, solve problems, adapt, communicate,… like humans. Currently, artificial intelligence is being applied in many fields, such as healthcare, finance, education, etc.
Some prominent products of artificial intelligence in life include: virtual assistant applications (Siri, Google Assistant), self-driving cars, social applications (Facebook, YouTube, …), … and many other products.
Currently, pursuant to Clause 6, Article 4 of the Vietnam Law on Intellectual Property 2005, as amended and supplemented in 2022, the subject of intellectual property rights is the owner of intellectual property rights or the organization or individual to whom the owner transfers intellectual property rights.
In addition, according to the provisions of Article 13 of the Law on Intellectual Property 2005, as amended and supplemented in 2022, on copyright, it is stipulated that authors are those who directly create part or all of a literary, artistic, and scientific work, including the following subjects:
Therefore, based on the above provisions, artificial intelligence is not the subject of intellectual property rights because it is a computer program, a product created by human hands, not an organization or individual, and does not have personal rights or property rights as prescribed in the Civil Code 2015.
The role of AI in innovation and intellectual property
Artificial intelligence cannot create work by itself; it needs human intervention, so it is difficult to recognize intellectual property rights for artificial intelligence products.
In many cases, artificial intelligence (AI) is capable of automatically creating works at the request of humans. Through machine learning and processing data from previous commands, AI can create works such as images, articles, or new music. However, AI is not currently recognized as a legal entity (either as an individual or a legal entity), so the question of who owns the works created by AI becomes a complex legal issue.
So the question is, in the above cases, how do we determine the owner of the work? Pursuant to the civil law of many countries, the intellectual property owner and author are individuals or organizations (legal entities). In the case of AI self-created, ownership is often attributed to:
Some countries have clearly defined AI ownership:
Products to be protected by intellectual property law must be creative, meaning they must be created by the owner and have not been published in any way.
However, the creation of a new work by artificial intelligence is not considered creative, because artificial intelligence will rely on the achievements and works created by humans to create another work. Therefore, currently, the application of artificial intelligence in creative and artistic fields such as literature, fine arts, etc. is facing great controversy.
In addition, the fact that artificial intelligence can create new work is also based on human algorithms, so it is difficult to consider artificial intelligence as the owner of that work. Based on the above analysis, it can be said that currently, Vietnamese law does not recognize the intellectual property rights of artificial intelligence.
It can be seen that the issue of intellectual property rights for works created by artificial intelligence is becoming a legal challenge, the source of conflicts and disputes over intellectual property rights. Especially the infringement of artificial intelligence on works created by humans.
This situation is happening not only in Vietnam but also all over the world. Currently, technologically developed countries such as the United States, Australia, etc. have not recognized the intellectual property rights of artificial intelligence. In addition, some other countries such as India, the UK, etc. recognize the intellectual property rights of programmers – the creators of artificial intelligence programs.
Currently, the law does not recognize intellectual property rights and does not protect rights to products created by artificial intelligence, so these products are outside the management of the law. Therefore, when applying artificial intelligence products, or exploiting those products, the law will not protect them.
In addition, the owner of artificial intelligence cannot commercialize products created by artificial intelligence to exploit and recover investment capital for research to improve and upgrade technology. Not only that, not recognizing products and inventions created by artificial intelligence will have no legal basis to resolve conflicts and disputes arising between humans and artificial intelligence.
Above is the entire answer of Viet An Law to the question: “Are intellectual property rights for artificial intelligence protected?”. If you need more detailed advice, please contact us to receive the most dedicated support.