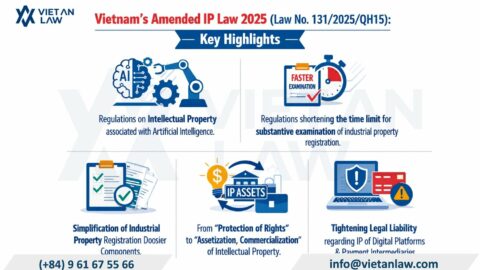
Nowadays, people often refer to the phrase “Brand strength – difference creates value”. It is said that brand is an important factor that every business investors are aiming to build for their products, services, including trademarks. Trademark is one of the factors that can has the strongest impact on consumer psychology. Have you ever wonderer: why are people willing to buy a bag with the trademark name LV for millions of dollars that other domestic bags only cost a few hundred thousand VND. It is not mainly in quality, the key difference is the trademark of the product.

It can be said that the importance of a trademark to goods and services today, Viet An Law will guide the basic regulations on a trademark registration in Vietnam following:
Visible mark is prescribed in Article 72 of the Vietnam Law on Intellectual Property 2005, amended and supplemented in 2009, it also stated that a registered trademark must have a “visble” sign. In the TRIPS agreement, “visible” means visually recognizable. The signs identified by hearing or tasting such as flavor, sound,… are invisible signs, so they cannot be used for trademark registration. The “visible” signs are divided into the following three basic groups:
The first manifestation of the two-dimensional signs is words, letters, characters, numbers, conventational symbols and slogans. This type of sign includes only readable elements: a sign contains one or more words, with or without meaning; conventional letters, characters, number or symbols; or a combination of such factors, including slogans and promotional messagess. These signs do not include any background, frame or visual elements. Letter signs also include personal signatures which can be real or stylized. Nowadays, many famous trademarks, especially fashion trademarks, often use stylized personal signatures to be their own trademark products. A figurative sign is a visible two-dimensional sign in a trademark registration, consisting of one or more two-dimensional visual elements such as logos, numbers, devices, abstracts or imaginary geometries or two-dimensional figures intentionally created. The color element is also considered a sign of trademark identification. However, simple shades that include only conventional words, letters, characters, numbers or symbols may make the trademark restrict to be registered because these factors have not yet reached the “distinguishability” of the products.
Nowadays, in trademark registration, people is using mixed signs, which is a combination of one or more words, letters, characters, numbers or conventional symbols with one or more many figure signs or non-written elements.
In trademark registration, colors recognized as a trademark must be represented by a specific shape or must have a clearly defined line combined in a uniform, defined and distinct manner.
Article 72 of the Law on Intellectual Property 2005 (amended in 2009) stipulates that a protected trademark is a sign visible in the form of a figure, word, three-dimensional or a combination expressed in one or more colors; this is also capable of distinguishing the trademark owner’s products or services from those of other subjects. Therefore, it is said that the law of Vietnam accepts the protection of colos as a trademark. However, in current of trademark registration in Vietnam, a single color or a set of colors that does not form a definite sign. That means it is not protected as a trademark. Generally, a color trademark is protected only when it is a figure, text, three-dimensional or combination sign represented by one or more of the colors.
Three-dimensional sign is a type of block sign that can be registered as a trademark, for example, shape of goods, product packings…
In order to be granted protection, the following types of three-dimensional signs can be distinctive, in the following specific forms:
Currently, according to the provisions of the Law on Intellectual Property 2005, amended and supplemented in 2009, simple geometries are not distinguishable. Therefore, simple geometries in three-dimensional space such as cube, sphere, cylinder, pyramid… are not recognized by Vietnamese law as a trademark.
Some of the famous three-dimensional trademarks such as: the monolithic flying horse of a Rolls-Royce, the floating lion of the Peugeot car,…. In addition, motion signs (cartoon) and holograms and “position” signs are also signs to identify trademark registration. A “position” sign may be further referred to as a figurative, composite, color or hologram sign attached to a particular part of or on a specific position on the goods to which the mark needs distinguishing. The trademark of this type is permanently fixed at the same position on the goods of the object bearing the trademark, according to the size or proportion corresponding to the size of goods. Position sign is a rather unique sign that has been registered in many countries around the world, but in Vietnam this sign is not widely used, there is almost no requirement for trademark registration.
According to the legal regulations on trademarks in Vietnam, only visible signs can be registered in Vietnam, thereby eliminating the possibility of registering trademarks of sounds, flavors, etc.
However, it can be said that in some countries around the world, signs of color, sound,… are still able to register, depending on the regulations of each country. Unlike the “visible” signs, the invisible signs are quite limited in the registration of the trademark, especially the registration ability of the invisible signs will depend on whether that sign can be represented graphically or not.
For example, according to Singapore’s Trademark Law, if the sign includes melodies, bells, noises, songs or other sounds, is clearly and accurately represented by a musical notation system, such these musical symbols must be accompanied by the trademark application and are so sufficient to satisfy the graphic representation requirement.
According to Vietnamese law, the distinguishing ability of trademarks is one of two important factors to consider and allow for trademark registration. A trademark is considered distinctive if it is composed of one or several recognizable, easy-to-remember elements or from many elements combined into a recognizable, easy-to-remember whole and does not belong to cases are considered indistinguishable according to the provisions of the law.
A trademark has the ability to distinguish from other trademarks for the same group, the same products and services not only to ensure the interests of consumers, but also to ensure the rights and interests of businesses. A trademark considered distinguishable must not fall into the following cases:
The trademark applicants may invoke distinguishable in opposition to the assessor’s decision to say that a sign is non-distinguishble, generic or descriptive. It is the applicant’s responsibility to prove, but the appraisal agency may supplement the evidence submitted by the applicant with any relevant information obtained from various sources.
Signs, which are deceptive or misleading when they are in use, are not registered for protection as trademarks for goods and services. A sign considered deceptive is that when used in trade associated with related goods or services, it will bring deceptive or misleading information about the goods or services. About this problem, these information is conveyed by signs relating to nature, object, quality, geographical origin, quantity, size, purpose, benefits, price, value or other relating to properties of goods and services.
Deception can be considered in the following aspects:
Signs of geographic deception: For example: Trademark “Moc Chau Thanh Ha fresh milk” may be rejected if the milk products are not related to Moc Chau. For this reason, the phrase “Moc Chau fresh milk” in the trademark may cause consumers to wrongly associate or guess about the origin of the product.
A trademark containing the words “ISO Certification”, or “Check-BSI” shall not be accepted for protection, if the organizations named in those trademarks have authority to issue that standards/certifications and they also disagree with the use of the trademark. Similarly, in Vietnam, the words “US technology”, “European standards” will be rejected because the registry thinks they can deceive the compliance with the standards.
These above are the current regulations on trademark registration in Vietnam, the regulations are the basic principles and standards applied at the trademark registration agency. However, these regulations do not decide on the results of substantive examination of a trademark application, or whether a trademark is registered or not, the trademark registration office still retains all powers in the evaluation and assessment of the possibility of a trademark registration.
Viet An Intellectual Property Agent provides IP service with the trademark registration, trademark renewal, patent registration and Law business consultant in Vietnam.
Table of contents