Patents play a key role in innovation and development. Patents not only promote innovation but also promote technology transfer. Reasonable commercial exploitation of this type of intellectual property will contribute to increasing benefits for society, promoting sustainable development, and improving national competitiveness. Patents are intangible assets and are protected and recognized by law. In the article below, Viet An Law Firm will present to clients about usage patent in Vietnam.
In the Trans-Pacific Partnership Agreement that Vietnam signed, in the section Related to Intellectual Property, specifically Article 18.37 TPP, this issue was mentioned as follows: “..each member country affirms that patents are granted for patents that are claimed by at least one of the following types: new uses for a known product, new methods of using a known product known, or new procedures for using a known product”.
Thus, according to the provisions of this article, Vietnam, a TPP signatory, will have to accept “usage patent” protection expressed in “product” or “process” claims of protection.
Article 3.12 of the Intellectual Property Law stipulates that: “A patent is a technical solution in the form of a product or process to solve a defined problem by applying natural laws.”
A usage patent is considered a type of patent in which the applicant not only creates a new product or process but also addresses how that product or process can be used or applied in reality.
Usage patents are often detailed descriptions of how a new product or method can be integrated into a practical environment, solve specific problems, or provide outstanding benefits to users. It is not limited to describing the structure or operating principle of the product, but also talks about how it can be deployed and applied in real-life situations.
Example of a usage patent
Patent name: Anti-abrasion coating and method of use
Patent Classification (IPC): C08K3/36, C09D7/12, C08K9/06, C08K3/22, B32B5/16
Applicant: PPG INDUSTRIES OHIO, INC.
Application date: March 31, 2003
Application announcement date: January 25, 2005
The patent relates to an anti-wear coating having high abrasion transparency. This filler contains a homogeneous mixture of particles, consisting of organic silane-treated alumina and similarly treated or untreated silica. The combined use of these particles allows to significantly reduce the weight percentage of anti-wear particles, creating appropriate abrasion resistance for the coating. These particles may have an inner face, for example, urethane acrylate binders, which may be solidified using UV radiation. The patent also covers methods of using this coating.
A patent is protected in the form of a patent if it meets the following conditions:
According to Article 59 of the Intellectual Property Law, the following subjects are not protected as patents:
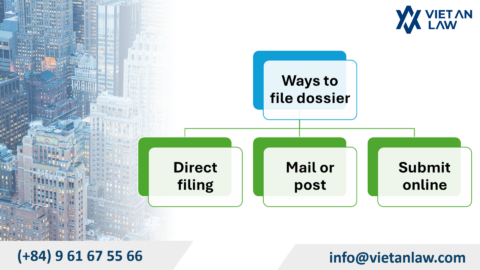
| Step 1: Receive application | Applications can be submitted directly or sent by post to the Intellectual Property Office headquarters in Hanoi or 2 Representative Offices of the Department in Ho Chi Minh and Da Nang. |
| Step 2: Formality examination | Check the compliance with the regulations on the form for the application, thereby concluding whether the application is considered valid or not (Decide to accept the application as valid/refuse to accept the application).
· In case the application is valid, the National Office of Intellectual Property issues a decision to accept the valid application; · In case the application is invalid, the National Office of Intellectual Property shall issue a notice of intention to refuse to accept the application, clearly stating the reasons and shortcomings that cause the application to be refused acceptance and setting a time limit of 2 months to accept the application. The applicant has comments or corrects errors. If the applicant does not correct the errors/corrects the errors unsatisfactorily/has no objections/unreasonable objections, the National Office of Intellectual Property will issue a decision to refuse to accept the application. |
| Step 3: Publication of the application | After a decision is made to accept a valid application, the application will be published in the Industrial Property Official Gazette. |
| Step 4: Substantive examination of the application | Conducted when there is a request for substantive examination;
Evaluate the ability of the subject matter stated in the application to be protected according to the protection conditions (novelty, level of creativity, industrial applicability), thereby determining the corresponding scope of protection. |
| Step 5: Decide to grant/refuse to grant a protection title | If the subject matter stated in the application does not meet the protection requirements, the National Office of Intellectual Property shall issue a decision to refuse to grant a protection certificate;
If the subject matter stated in the application meets the protection requirements, and the applicant pays the fees and charges in full and on time, the National Office of Intellectual Property shall issue a decision to grant a protection title and record it in the National Registration of Patents and publication in the Industrial Property Official Gazette. |
If you have questions or need advice on legal services related to patent registration and usage patent in Vietnam, please contact Viet An Law for the best support!