Foreign citizens and stateless persons who are permanently residing in Vietnam may acquire Vietnamese nationality. From July 1, 2025, the Law amending and supplementing a number of articles of the Law on Vietnamese Nationality – passed by the 15th National Assembly at the 9th Session – officially takes effect, with many new regulations, including regulations on conditions for acquiring Vietnamese nationality. Below, Viet An Law provides an update on notable new regulations on Conditions for Vietnamese Citizenship from 2025.
Table of contents
According to Clause 5, Article 1 of the 2025 amended Law on Vietnamese Nationality, effective from July 1, 2025 (amending and supplementing Article 19 of the 2008 Law on Vietnamese Nationality), the conditions for acquiring Vietnamese nationality are stipulated as follows:
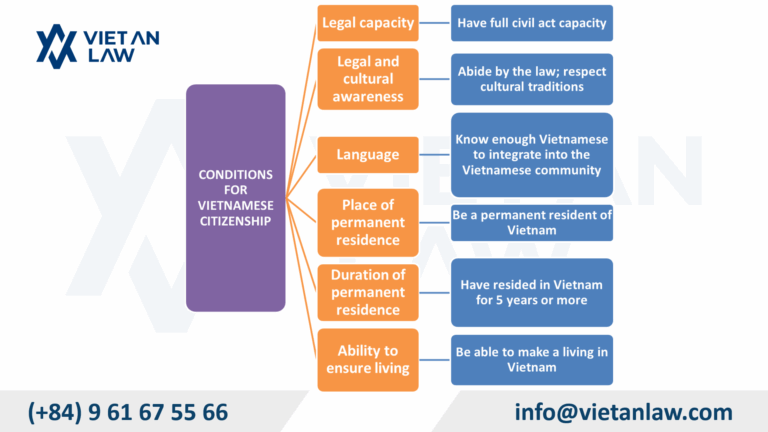
Foreign citizens and stateless persons who apply for Vietnamese nationality may be granted it if they meet the following conditions:
Compared to the provisions of Clause 1, Article 19 of the 2008 Law on Vietnamese Nationality, this provision has the following new points:
A person applying for Vietnamese nationality whose spouse or biological child is a Vietnamese citizen may be granted Vietnamese nationality without having to satisfy conditions (3), (5), and (6).
A person applying for Vietnamese nationality who falls into one of the following cases may be granted Vietnamese nationality without having to satisfy conditions (3), (4), (5), (6):
Thus, the new regulation has added that if the paternal/maternal grandparents are Vietnamese citizens, the grandchildren can be naturalized in Vietnam. At the same time, many cases are exempted from the usual conditions for naturalization, such as knowing Vietnamese enough to integrate into the Vietnamese community; being a permanent resident in Vietnam; having resided in Vietnam for at least five years at the time of applying for Vietnamese nationality; being able to ensure a living in Vietnam… These changes aim to create favorable conditions for foreign investors, scientists, and experts to be naturalized in Vietnam under more flexible criteria, thereby attracting high-quality human resources.
It should be noted that people applying for Vietnamese nationality in these cases are allowed to retain their foreign nationality if they meet the following conditions and are permitted by the President:
Previously, the 2008 Law on Vietnamese Nationality had a strict regulation: “A person applying for Vietnamese nationality must have a Vietnamese name”. However, the new regulation allows naturalized people to combine their Vietnamese name with a foreign name. Specifically: “In the case of a person applying for Vietnamese nationality and at the same time applying to retain their foreign nationality, they can choose a name that combines their Vietnamese name and a foreign name. The name is chosen by the person applying for Vietnamese nationality and is clearly stated in the Decision on granting Vietnamese nationality.”
This regulation aims to ensure convenience for individuals living and working in countries where they also hold citizenship, while also ensuring international integration. Currently, many countries stipulate that names can both ensure elements of the country they are naturalized in and have elements of the tradition of the country they were born in, for example, in France or the US, the names can be Matthew Nguyen or Robert Tan.
Clause 2, Article 1 of the 2025 amended Law on Nationality has also added the Identity Card and Electronic Identity as documents proving Vietnamese nationality. This is in addition to paper documents such as Birth Certificates, Passports, Decisions on Naturalization, Decisions on Reinstatement of Nationality, and Decisions on Adoption, which were already stipulated in Article 11 of the 2008 Law on Nationality.
The settlement of naturalization dossiers stipulated in Clause 2, Article 21 of the 2008 Nationality Law is amended by Clause 7, Article 1 of the 2025 amended Nationality Law in the direction of shortening the time as follows:
In addition, the 2025 amended Law on Nationality also adds a provision: Within 20 days from the date of receiving a complete and valid dossier, the Vietnamese representative agency abroad is responsible for examining the documents in the application for Vietnamese nationality and transferring the dossier with its proposal for Vietnamese nationality to the Ministry of Justice; at the same time, send information to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs to coordinate in performing the state management function on nationality. The Ministry of Public Security is responsible for verifying the identity of the person applying for Vietnamese nationality at the request of the Ministry of Justice.
Above is an update of the new regulations on conditions for Vietnamese Citizenship from 2025. If you have any related questions or require legal advice on civil status matters, please contact Viet An Law for professional guidance and support!




